Metal stamping is an indispensable manufacturing technology underpinning nearly every modern vehicle platform. From advanced structural reinforcements to precision electrical terminals, stamped components deliver the accuracy, repeatability, and cost efficiency required by global automakers. As the automotive sector accelerates toward lightweighting, electrification, and digitalized production, the role of an advanced custom metal stamping company has become not merely supportive—but strategically critical.
This article offers a deep technical perspective on the manufacturing processes, engineering capabilities, and supply chain value that high-end metal stamping providers bring to automotive OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers.
Automotive manufacturers depend on metal stamping technology for its unique combination of dimensional precision, material versatility, and scalability. Stamping enables rapid, cost-effective mass production while meeting stringent tolerance requirements essential for safety-critical and mission-critical systems. When coupled with modern simulation tools, advanced die design, and automated production lines, stamping becomes an engineering discipline capable of producing complex geometries at extraordinary volumes.
For additional industry insights, automotive engineers may consult the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE)
Stamped components appear across all major vehicle subsystems, including:
Body-in-white reinforcement brackets and crash-structure elements
EV battery housings and thermal-shielding components
Electrical terminals, connectors, and metal spring components
Powertrain and driveline support structures
Interior mechanisms, hinge components, seat system assemblies
Each category demands precise forming behavior, consistent mechanical performance, and high durability over the vehicle life cycle.
Modern stamping offers:
Exceptional repeatability with micron-level control
High-volume production at optimized cost-per-piece
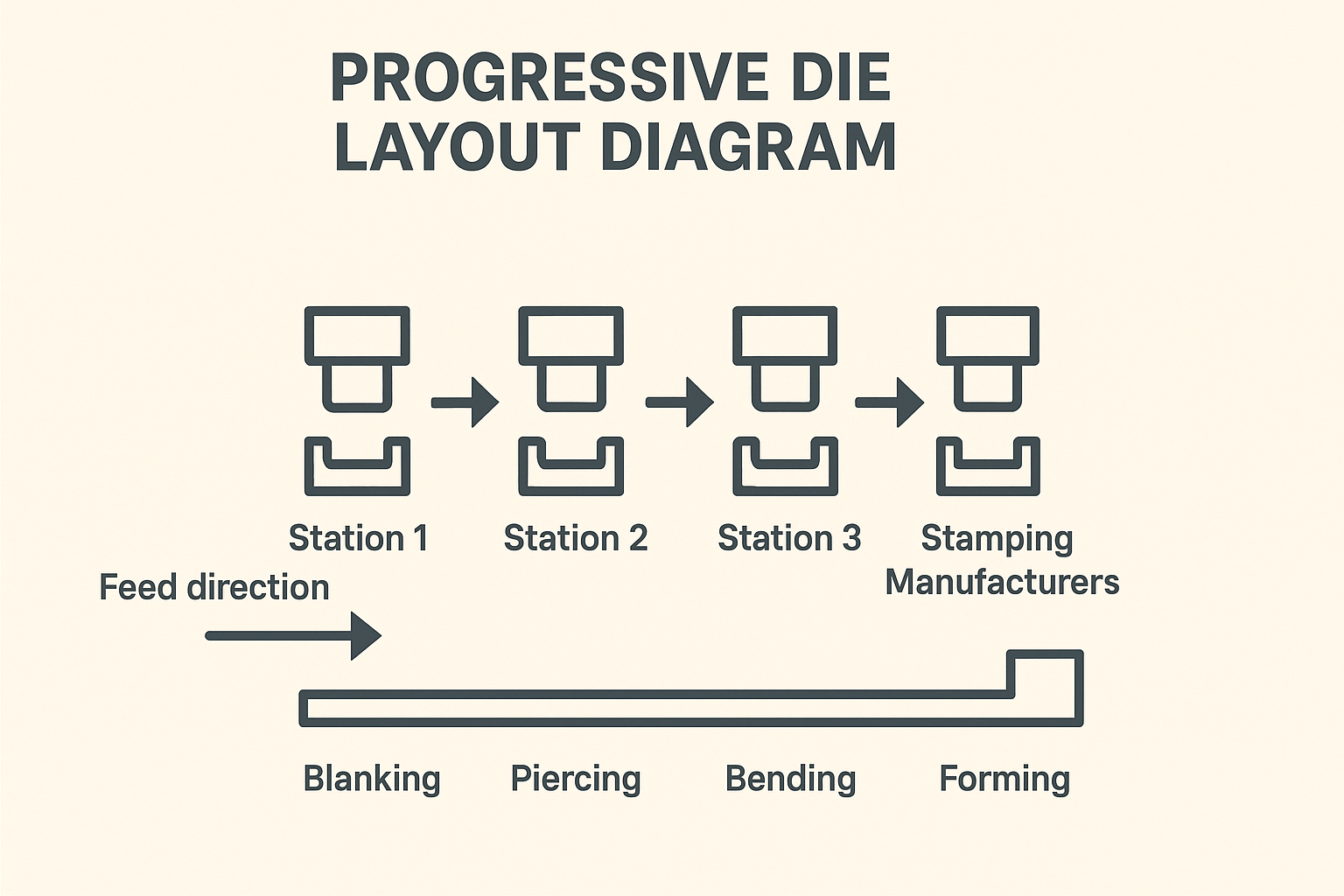
Complex bending and forming achievable through multi-slide or progressive-die systems
Material efficiency, especially in high-strength steel and aluminum applications
Process reliability backed by IATF 16949 and PPAP compliance
For metallurgy references and materials comparison data, engineers may reference: https://www.matmatch.com/
Leading stamping companies collaborate closely with OEM engineering teams to determine:
Material formability (HSS, dual-phase steels, aluminum alloys)
Finite-element forming simulations to predict wrinkling, thinning, and springback
Tolerance chain management for assembly-critical components
Optimal forming sequences for progressive, transfer, or multi-slide stamping
This early involvement significantly reduces downstream tooling costs and accelerates production readiness.
Manufacturing excellence in stamping is inseparable from die engineering. Tool steels such as D2, DC53, and powder-metallurgy grades are selected based on wear resistance, compressive strength, and temperature tolerance.
The die manufacturing workflow typically includes:
CAD/CAM design modeling
High-precision CNC milling for cavity accuracy
EDM finishing for intricate geometries
Stress-relief heat treatment to stabilize dimensional integrity
Try-out iterations to refine forming behavior
Before production, incoming materials undergo:
Mechanical property testing (yield strength, elongation, tensile strength)
Surface evaluation for coatings, roughness, and corrosion resistance
Dimensional and thickness validation
These parameters directly influence forming consistency and die longevity.
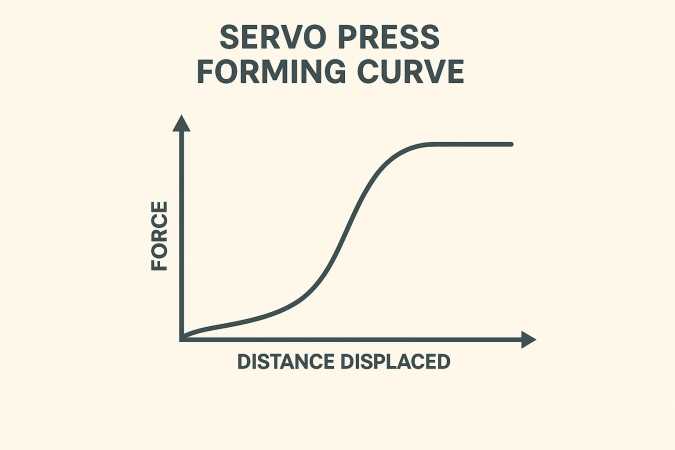
Automotive stamping lines may range from 80-ton up to 2,500-ton capacity. Many manufacturers now employ servo-driven presses that enable:
Programmable forming curves
Reduced vibration and improved edge quality
Superior control over deep-drawing and high-strength steel forming
Inline load monitoring, automated coil feeding, and high-speed transfer systems ensure stable, continuous production output. Complex geometries are formed through synchronized multi-stage processes designed to achieve the final desired shape with minimal scrap.
Automotive stamping must comply with stringent quality frameworks such as:
PPAP (Production Part Approval Process)
SPC (Statistical Process Control)
APQP (Advanced Product Quality Planning)
CPK analysis for dimensional capability
Inline optical inspection for real-time defect detection
To review quality standards used across automotive manufacturing, refer to:
https://www.iatfglobaloversight.org/
A competitive stamping provider features:
High-tonnage presses suitable for structural automotive components
Multi-slide and fourslide systems enabling intricate part forming
Capacity for both low- and high-volume production
Automated assembly, welding, and secondary finishing
Superior manufacturers excel in:
Rapid prototyping transitions to production
Material utilization optimization and scrap reduction
CAD/CAE integrated tool design
Die life extension via coatings and lubrication systems
Stamped products required by automotive OEMs and Tier suppliers include:
Complex brackets and chassis reinforcements
Deep-drawn enclosures for EV battery and power electronics
Electromechanical terminals and precision connectors
Heat shields, grounding plates, and sensor housings
For engineering support or prototype-to-production machining solutions, your team may reference:
https://www.mtcncservices.com/
(MAXTECH CNC Services provides precision machining that complements stamping processes for hybrid assemblies and engineered metal components.)
Automotive supply chains demand more than mechanical accuracy. Critical purchasing factors include:
Full traceability of coil materials
Consistent surface and coating quality
Corrosion protection, packaging durability, and export readiness
Cost modeling: tooling amortization vs. per-piece economics
Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI) and Just-in-Time (JIT) delivery
Long-term capacity scalability to align with vehicle launch schedules
Establishing a supplier that integrates technical capabilities with industrial-grade logistics is essential for stable automotive program execution.
EV platforms require:
Battery tray structures
High-precision shielding components
Lightweight brackets for ADAS sensors
As vehicles demand stronger yet lighter structures, stamping must handle:
Ultra-high-strength steels (UHSS)
Multi-phase steels for crash structures
New technologies include:
IoT-enabled press monitoring
Predictive maintenance for die sets
Digital twins for tooling lifecycle optimization
Manufacturers are improving:
Scrap recycling systems
Lubrication and coating efficiency
Die-life improvements through surface engineering
For engineering news and advanced manufacturing updates:
https://www.engineering.com/
Automotive OEMs and Tier suppliers depend on metal stamping manufacturers that combine process mastery, engineering collaboration, and system-level supply chain reliability. The maturity of a stamping company’s manufacturing process directly determines component consistency, durability, and cost efficiency—ultimately influencing vehicle safety and production economics.
Selecting a competent stamping partner is therefore not merely a procurement decision; it is a strategic engineering choice that can significantly impact the success of an automotive program.