In modern vehicle development, few fabrication methods shape the automotive landscape as fundamentally as stamping. Whether the goal is structural rigidity, lightweight enclosures for electrified platforms, or precision-formed terminals for electronic modules, stamping remains the backbone of high-volume component creation. Its effectiveness does not stem solely from high-speed presses. Instead, it results from a sophisticated manufacturing ecosystem in which engineering collaboration, die craftsmanship, controlled sheet-material behavior, and multi-stage forming converge.
This article presents an end-to-end explanation of how a stamping provider supports automotive producers through advanced forming processes, refined tool engineering, robust material validation, and scalable production systems. For automakers striving for cost-efficient and stable component supply, understanding this process is essential.

To serve the automotive field reliably, a stamping provider must do far more than press sheet materials into basic shapes. The process extends from early design guidance to forming simulation, die development, material selection, high-tonnage press operation, and performance verification under strict production standards.
By shifting the focus from “what stamped parts are” to “how stamped parts are engineered and produced,” automotive teams gain deeper insight into why some stamping suppliers deliver consistent results while others fall short.
This article offers precisely that perspective: a comprehensive guide on how a modern stamping provider integrates forming technology, tooling craftsmanship, materials science, and mass-production flow to support the automotive industry.
Stamped parts appear across virtually every subsystem of a vehicle. Using sheet materials and alloys, stamping providers create:
High-strength brackets that reinforce body-in-white structures
Lightweight housings for electric-vehicle battery modules
Electrical terminals that require exceptional dimensional precision
Sensor mounting plates and shielding elements for ADAS and power electronics
Interior mechanisms and functional assemblies requiring repeatable operation
These components must satisfy demanding mechanical, thermal, and durability requirements, especially in structural and electrically conductive applications. The forming process must therefore be both controlled and predictable.
The appeal of stamping lies in the combination of accuracy, efficiency, and scalability. Compared with subtractive or casting-based processes, stamping provides:
Dimensional consistency across tens of thousands—even millions—of parts
High-speed production, enabled by continuous feeding and multi-stage forming
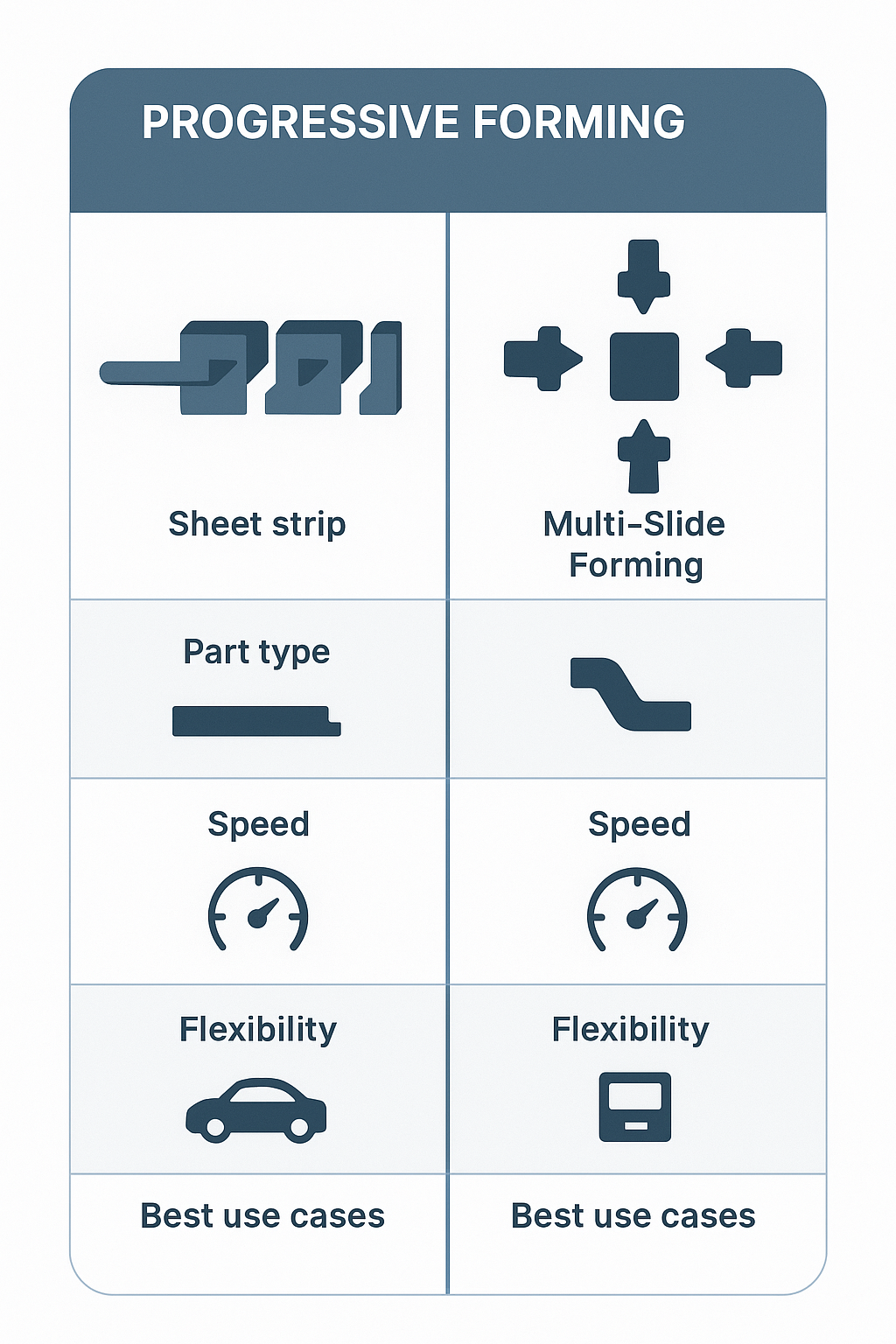
Process strengths that support intricate shapes achievable only with progressive or multi-slide forming
Material efficiency, particularly for high-strength steel and lightweight alloys
Reliable performance that meets automotive production standards from PPAP to ongoing CPK control
In a sector where cost, structural performance, and weight optimization must be balanced, stamping remains essential.
Collaboration between automotive producers and stamping providers begins long before material reaches the press. Engineers evaluate how a component’s geometry behaves during forming, examining potential thinning, wrinkling, or springback. Simplified simulation tools predict forming risks, enabling adjustments to radii, draft, or bend sequences before tooling investment begins.
This early alignment ensures that tooling reflects realistic material behavior rather than assumptions. It also accelerates program launch, reducing the number of die adjustments required during try-out.
A stamping provider’s die-engineering proficiency often determines whether a part can be manufactured reliably. Tooling relies on engineered materials such as high-hardness tool steels, chosen for their wear resistance and dimensional stability.
The die-making workflow includes:
CAD modeling of die geometry
CNC machining of die cavities and forming surfaces
EDM finishing for tight internal features
Heat treatment for dimensional stabilization
Progressive try-out sessions to refine shape control
Die engineers evaluate how the sheet material flows, where pressure must increase or decrease, and how binder forces must be balanced. This iterative refinement is essential to achieving repeatable forming performance under full production loads.
Before forming begins, sheet materials undergo multiple validation steps, ensuring they behave predictably under load. These checks include:
Strength, elongation, and yield-stress measurements
Thickness and flatness verification
Surface evaluation for coatings or protective films
Confirmation of lubrication compatibility for forming operations
Since automotive parts often rely on high-strength steels or advanced lightweight alloys, these verifications are crucial. Any deviation in material performance can result in dimensional distortion or premature die wear.
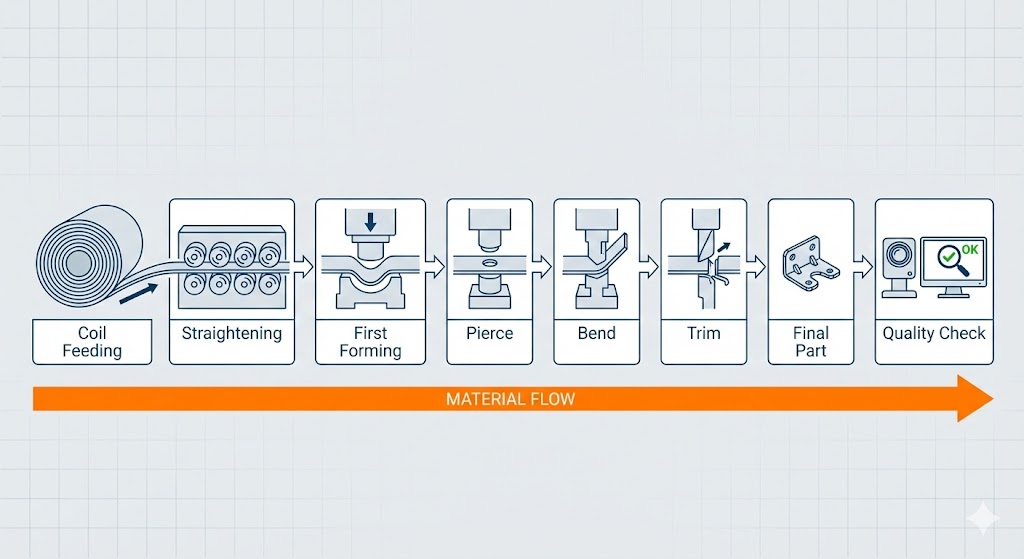
At the heart of the stamping process lies the forming press. Modern lines incorporate servo-driven presses that allow engineers to program forming curves with greater precision than traditional mechanical systems. Servo presses can reduce vibration, optimize dwell time for deep-draw sections, and improve edge integrity for parts with stringent bending requirements.
Key features of press-line operation include:
Automated coil feeding for continuous production
Progressive die stages that form, pierce, bend, coin, and trim in a coordinated sequence
Multi-slide forming heads for complex geometries
Real-time monitoring of load profiles, lubrication, and forming forces
Through these control systems, providers ensure stable output even during high-volume runs.
Automotive producers expect stamped components to meet strict performance standards. To achieve this, stamping providers employ:
Optical measurement systems for rapid, non-contact dimensional analysis
Coordinate-measuring machines for high-accuracy verification
Production-approval frameworks such as PPAP
Statistical monitoring tools like SPC and CPK
Routine audits to align with automotive production standards
These systems ensure that every part conforms to dimensional, functional, and surface-finish requirements throughout the entire program lifecycle.
A leading stamping supplier offers:
Press ranges supporting thin-gauge terminals, structural elements, and large assemblies
Multi-slide forming for intricate geometries that cannot be produced in conventional presses
Automation-driven loading and unloading for stable throughput
Tool-monitoring systems that extend die life and reduce downtime
Beyond mechanical systems, engineering expertise is a defining factor. Strong providers excel in:
Fast prototyping with smooth progression to mass production
Sheet-material path optimization to reduce waste
Long-run stability under demanding conditions
Controlled lubrication and temperature management to maintain forming predictability
These strengths differentiate capable stamping firms from low-tier competitors.
Automotive producers rely on a wide range of tailored stamping services, including:
Progressive forming for structural brackets and mounting plates
Deep-draw forming for EV housings and protective enclosures
High-precision terminals from conductive alloys for power-distribution systems
Shielding components designed for electromagnetic and thermal protection
Secondary processing such as tapping, welding, and surface finishing
These services support both prototype builds and full-scale vehicle programs.
For procurement departments managing complex vehicle platforms, selecting the right stamping supplier involves more than evaluating unit prices. Key considerations include:
Full traceability for coils and sheet batches
Compliance with packaging, corrosion resistance, and international transport standards
Tooling amortization strategies aligned with production volumes
Inventory management through JIT or VMI systems
Long-term stability for multi-year vehicle programs
Automotive supply chains reward reliability, not just cost efficiency.
The automotive sector is undergoing rapid transformation, and stamping processes are evolving accordingly:
EV platforms introduce new stamped components such as battery frames, cooling-plate housings, and precision shielding plates.
New lightweight alloys and ultra-high-strength steels require more sophisticated forming strategies.
IoT-enabled presses enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and automated correction of forming variations.
Providers are implementing more efficient lubrication systems, energy-optimized forming cycles, and advanced scrap-recycling programs.
The success of a stamping provider does not hinge solely on equipment or materials. It is the integration of engineering insight, die craftsmanship, material control, forming precision, and performance verification that determines consistent outcomes.
For automotive producers, selecting a stamping partner with mature process strength is a strategic decision that directly influences component stability, program timing, and long-term production economics.
In an era defined by electrification, lightweighting, and globalized supply chains, a stamping supplier that excels in process execution becomes an irreplaceable asset.